The Open System Interconnection model or normally known as the OSI model is one of the important topics in networking classes. The OSI model is the back bone of networking. All the protocols and connecting is made of OSI layers. This particular subjects seems to be a pain in the ass for the most of the students and they do not practice using the layers in the OSI model. Since the basics of their networking is not so strong, they tend to flip in their networking career. Here is my Advice for networking students PLEASE REMEMBER OSI MODEL. You guys will be using it the entire networking career.
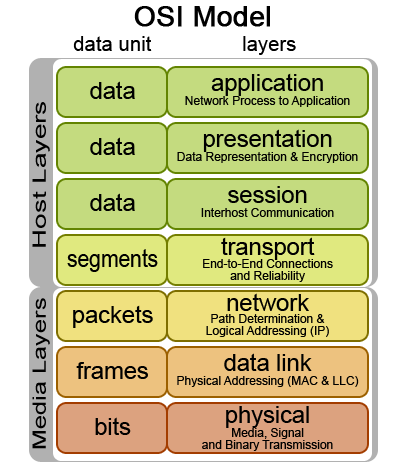
Let's get it started. OSI model consist of 7 layers. Application layer, presentation layer, session layer, transport layer, network layer, data link layer and physical layer. If you find it hard to remember those layers, do not worry as you keep practicing you should be able remember it. I normally use a sentence to remember the OSI layers - 'Please Do Not Trust Sales Person Always'. So, in this way I would not forget the OSI layers. Knowing the layers does not make you look good but you need to know the content of the each layer.
Before we jump into the layers, you guys need to know about Protocol Data Unit (PDU). Think of PDU like when some asks you what is your weight? and you answer 65 Kg. So, in this case PDU will be Kg. In the OSI model as the information travels through the layers it will take different forms. To address the different form of information we use PDU. OSI model has 3 approaches-1. Top to Bottom 2. Bottom to Top 3. Divide and Rule. It does not what is your approach as long you understand the layers. In this article I will take the Top to Bottom approach.
Application Layer
This the layer where the human interacts with the computer to send or receive something.In this layer we have networking applications like web browser and email,i.e. Firefox, Google Chrome, Safari, Internet Explorer, Gmail, Yahoo Mail etc. Basically in this layer your computer receives information from user or displays information for the user, thus the PDU in this layer is User Data.
Presentation Layer
This layer helps to convert the user data into computer readable format. In this layer, you will have your user data converted, encrypted and compressed. Who makes it all possible is your Operating System (OS). Your OS is sandwiched between your hardware and software. How does your word processor i.e. Microsoft Word know what are you typing and displays on the screen? This is all possible because the converting process is done by your OS. To help your remember what happens in this layer think of OS and what is does. PDU in this layer is Formatted Data.
Session Layer
Session layer helps to establish, maintain and terminate communication with the other networking device. There are three types of session.
1. Simplex - Think of keyboard (Sends or Transmits) and monitor (Receives) its a one way communication.
2. Half-Duplex- Think of walkie-talkie where both also can act as transmitter and receiver but one has to wait to transmit or receive until the other side has finished talking or receiving.
3. Full-Duplex - Think of telephone, you can speak and listen at the same time. One can be transmitter and receiver at the same time.
Transport Layer
The big chunk of formatted data will be received from session layer. The formatted data will be cut into few parts of small pieces. We call that segmentation. In a nut shell this layer breaks up the data from the sending host and then reassembles in the receiving host. PDU in this layer is Segments.
Network Layer
Network layer also known as layer and sometimes as 'Cisco Layer'. The device in this layer is router. So, basically if you know what is the function of a router, you will be able to explain this layer without problem. Segments will be received from transport layer and encapsulated. Think of encapsulation as putting a bread into a container. The same way the segments are put into packets and its called encapsulation. In this layer also we have, packet forwarding, packet filtering, Determines best path to send the packets (OSPF) and inter-network communication. PDU in this layer is Packets.
Data Link Layer
Data Link layer receives the packets from network layer. This layer consists of switch,network interface card (NIC) and ethernet port. If you know what is the function and use of each of the device, then data link layer shouldn't be a problem. Performs a physical addressing. The physical address is got from the NIC. So, if you know the use of the device you will be able to explain this layer. Logical Link Control (LLC) performs link establishment (switch) and Access to media using MAC address. Here the packets will be put into frames. The next layer is the physical layer and physical layer can only understand bits. So, data link layer turns frames ===>bytes===>bits while sending to physical layer and changes vice-versa when receiving from physical layer. Here we say, the data is transferred bits by bits to physical layer. PDU is Frames.
Physical Layer
Physical layer receives the data from data link layer bits by bits. The device present in this layer is cables. The job of the this layer is move bits between the device. PDU in this layer is Bits.
That is all about OSI Model. Learn it and know it by heart and I am sure it will be worth full.
Please feel free to ask me any question regarding the OSI model. I will be more than happy to help you out.Cheers.
Let's get it started. OSI model consist of 7 layers. Application layer, presentation layer, session layer, transport layer, network layer, data link layer and physical layer. If you find it hard to remember those layers, do not worry as you keep practicing you should be able remember it. I normally use a sentence to remember the OSI layers - 'Please Do Not Trust Sales Person Always'. So, in this way I would not forget the OSI layers. Knowing the layers does not make you look good but you need to know the content of the each layer.
 |
| The Seven Layers of OSI Model |
Before we jump into the layers, you guys need to know about Protocol Data Unit (PDU). Think of PDU like when some asks you what is your weight? and you answer 65 Kg. So, in this case PDU will be Kg. In the OSI model as the information travels through the layers it will take different forms. To address the different form of information we use PDU. OSI model has 3 approaches-1. Top to Bottom 2. Bottom to Top 3. Divide and Rule. It does not what is your approach as long you understand the layers. In this article I will take the Top to Bottom approach.
Application Layer
This the layer where the human interacts with the computer to send or receive something.In this layer we have networking applications like web browser and email,i.e. Firefox, Google Chrome, Safari, Internet Explorer, Gmail, Yahoo Mail etc. Basically in this layer your computer receives information from user or displays information for the user, thus the PDU in this layer is User Data.
Presentation Layer
This layer helps to convert the user data into computer readable format. In this layer, you will have your user data converted, encrypted and compressed. Who makes it all possible is your Operating System (OS). Your OS is sandwiched between your hardware and software. How does your word processor i.e. Microsoft Word know what are you typing and displays on the screen? This is all possible because the converting process is done by your OS. To help your remember what happens in this layer think of OS and what is does. PDU in this layer is Formatted Data.
Session Layer
Session layer helps to establish, maintain and terminate communication with the other networking device. There are three types of session.
1. Simplex - Think of keyboard (Sends or Transmits) and monitor (Receives) its a one way communication.
2. Half-Duplex- Think of walkie-talkie where both also can act as transmitter and receiver but one has to wait to transmit or receive until the other side has finished talking or receiving.
3. Full-Duplex - Think of telephone, you can speak and listen at the same time. One can be transmitter and receiver at the same time.
PDU in this layer is still Formatted Data as no changes occurs to the data.
Transport Layer
The big chunk of formatted data will be received from session layer. The formatted data will be cut into few parts of small pieces. We call that segmentation. In a nut shell this layer breaks up the data from the sending host and then reassembles in the receiving host. PDU in this layer is Segments.
Network Layer
Network layer also known as layer and sometimes as 'Cisco Layer'. The device in this layer is router. So, basically if you know what is the function of a router, you will be able to explain this layer without problem. Segments will be received from transport layer and encapsulated. Think of encapsulation as putting a bread into a container. The same way the segments are put into packets and its called encapsulation. In this layer also we have, packet forwarding, packet filtering, Determines best path to send the packets (OSPF) and inter-network communication. PDU in this layer is Packets.
Data Link Layer
Data Link layer receives the packets from network layer. This layer consists of switch,network interface card (NIC) and ethernet port. If you know what is the function and use of each of the device, then data link layer shouldn't be a problem. Performs a physical addressing. The physical address is got from the NIC. So, if you know the use of the device you will be able to explain this layer. Logical Link Control (LLC) performs link establishment (switch) and Access to media using MAC address. Here the packets will be put into frames. The next layer is the physical layer and physical layer can only understand bits. So, data link layer turns frames ===>bytes===>bits while sending to physical layer and changes vice-versa when receiving from physical layer. Here we say, the data is transferred bits by bits to physical layer. PDU is Frames.
Physical Layer
Physical layer receives the data from data link layer bits by bits. The device present in this layer is cables. The job of the this layer is move bits between the device. PDU in this layer is Bits.
That is all about OSI Model. Learn it and know it by heart and I am sure it will be worth full.
Please feel free to ask me any question regarding the OSI model. I will be more than happy to help you out.Cheers.